In order to use the Secure Message delivery channel, the channel must be configured in Connect first
Configuring a Secure Message Delivery Channel
To configure a Secure Message delivery channel:
- Navigate to the Company Admin screen.
- Under the Campaigns sub-menu in the menu bar on the left, click on
the Delivery Channels menu item. The Delivery Channels screen
appears.
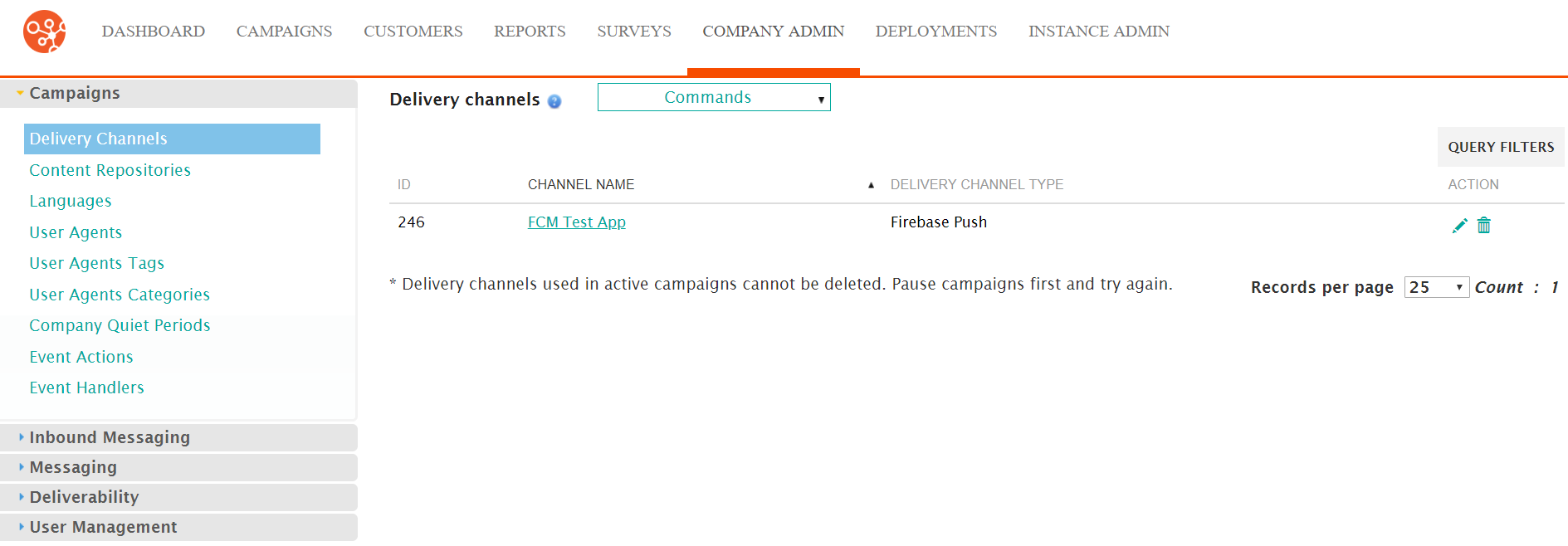
- From the Commands dropdown, select New Delivery
Channel.
The Configure Delivery Channel screen appears.
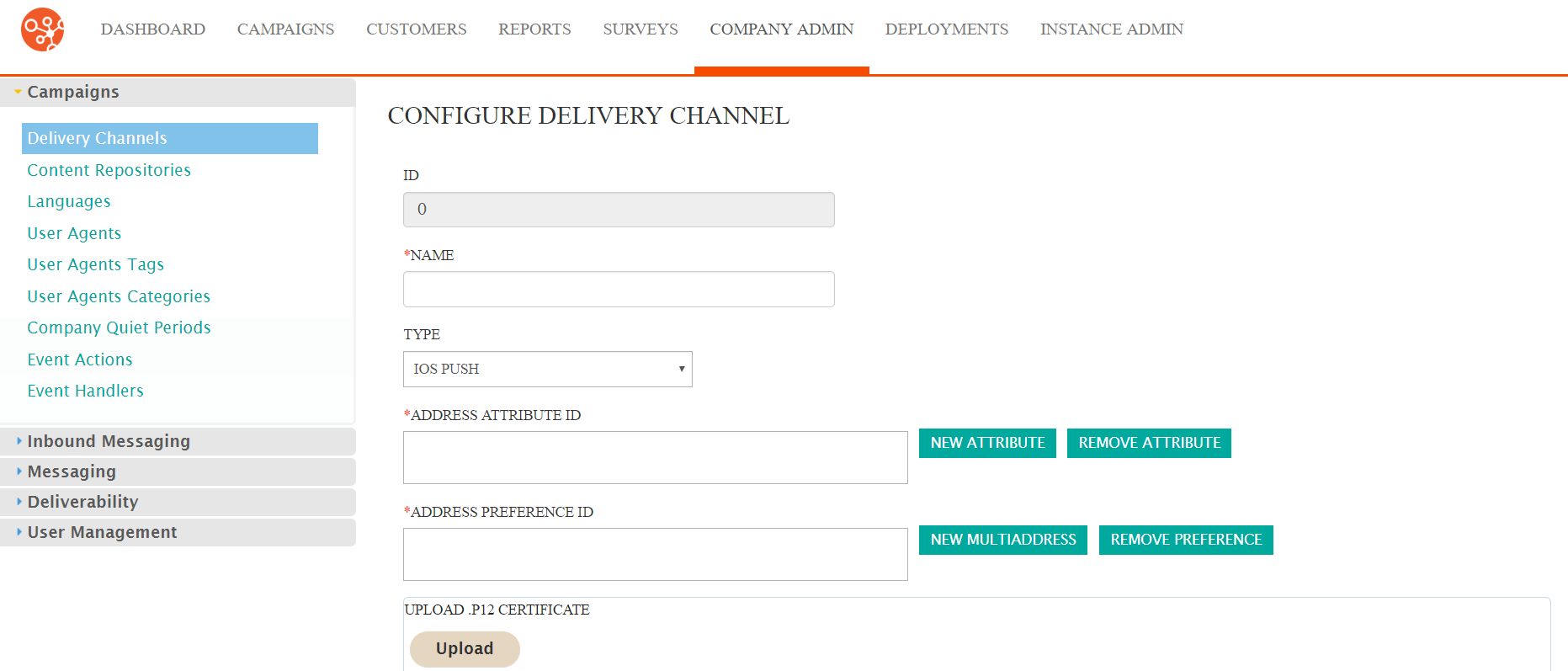
- Enter the details for the delivery channel:
- Name: A unique name for the delivery channel
- Type: The type of delivery channel, in this case select Secure Message
- Enter the desired customer attribute associated with the customer address in the Address Attribute ID field. For more information on adding attribute-specific information in the Address Attribute ID field, please see Creating Delivery Channels.
- Enter the desired customer preference associated with the customer address in the Address Preference ID field. For more information on adding preference-specific information in the Address Preference ID field, please see Creating Delivery Channels.
- Enter a MultiAddress preference if desired by clicking the New MultiAddress button. For more information on adding MultiAddress-specific information in the Address Attribute ID field, please see Creating Delivery Channels.
- Configure the endpoint by following the instructions for Configuring a Database Secure Endpoint or a Database Stored Procedure Endpoint or Configuring a Message Queue Secure Endpoint below as appropriate.
- Click the Save button. The Secure Message delivery channel is created.
Configuring a Database Secure Endpoint or a Database Stored Procedure Endpoint
When the secure endpoint is a database table or stored procedure, you must provide
Connect with the following information:
- The connection and login information required to connect to the database
- The database query used to store the message in the table, or to pass the message to the stored procedure
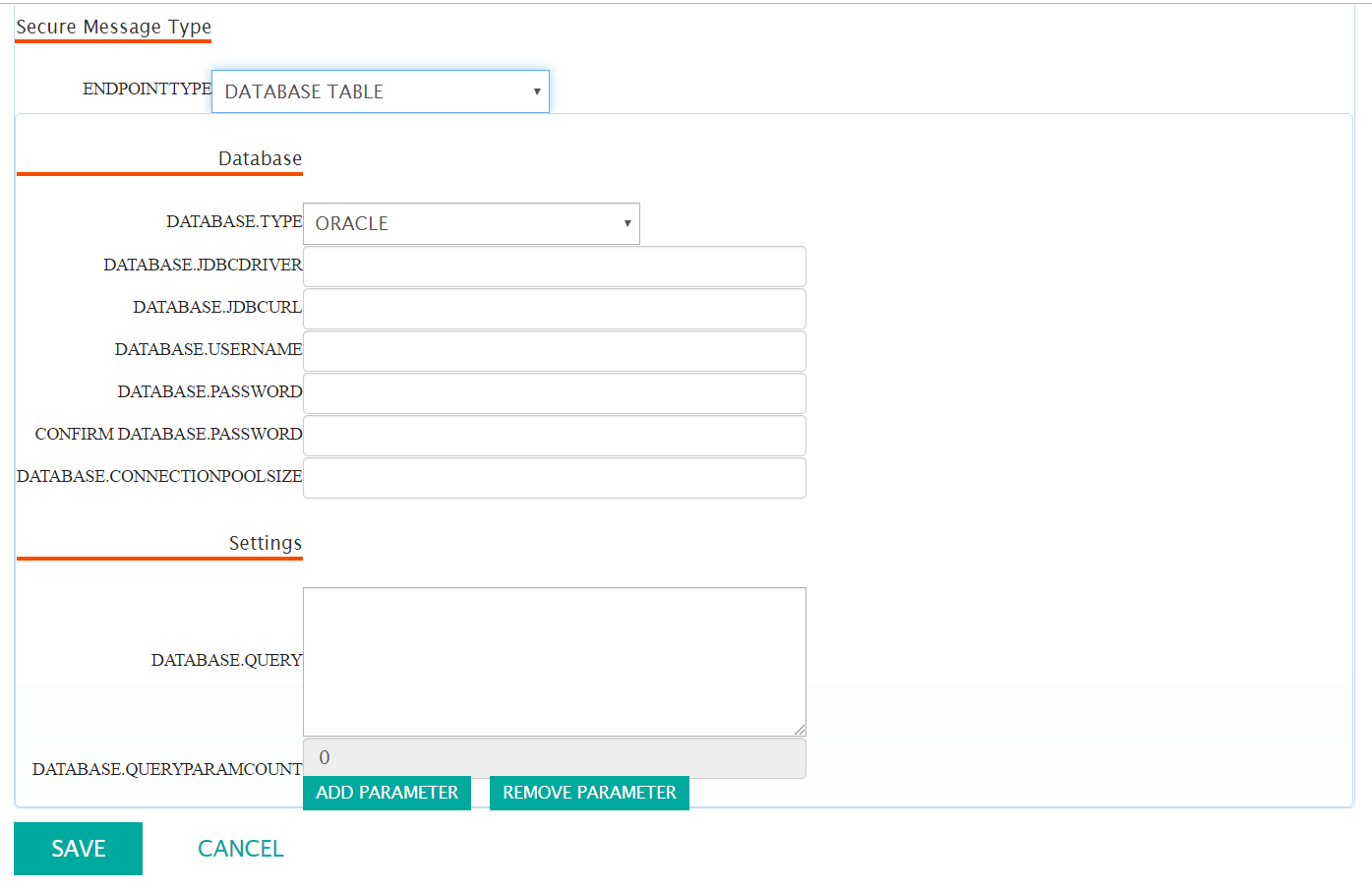
The database contact information consists of the following:
- Database type
- JDBC driver class
- JDBC URL to the database
- Database username and password
- Connection pool size
Each outside node will have a separate connection pool so the total number of
connections will be the connection pool size times the number of send nodes. When
the endpoint is a database query, the query will be parsed by the JDBC prepareStatement method. The query
will likely be a SQL INSERT statement such as the following:
INSERT INTO MY_MESSAGE_TABLE (CUSTOMER_KEY, MESSAGE) VALUES (?,?)
Note: The
'?' characters represent parameters to the query that will be supplied at
runtime.
When the endpoint is a stored procedure, the query will be parsed by the JDBC prepareCall method. The query will
likely be a statement such as the following:
{ call MY_STORED_PROC (?,?) }
Once you have set the query, you must configure values for each query parameter. Click the Add Parameter
button to create the right number of parameters. For each parameter, set the type and the value. Each value expression
may include the following variables which are set at runtime:
- customer_id
- instance_id
- event_queue_id
- email -- the string representation of the message
- message_definition - an internal object describing the message
- message_object - an internal object representing the message; the string representation is generated from this
- current_time_millis - a Java Long object set to the current time in milliseconds since January 1, 1970.
To remove a parameter that is not used, or was created erroneously, click the Remove Parameter button.
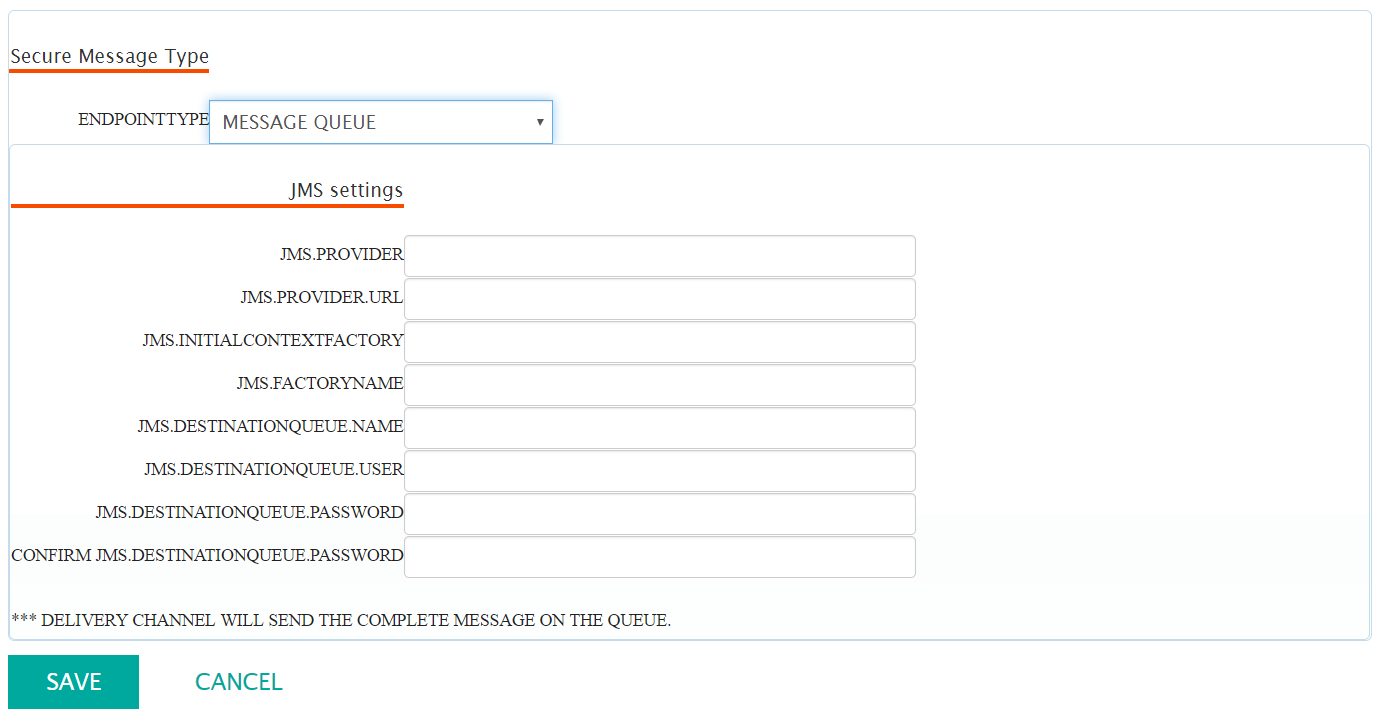
Configuring a Message Queue Secure Endpoint
When the secure endpoint is a message queue, you must provide the information needed
to connect to the queue using the Java Messaging Service (JMS) API. This information
consists of the following:
- JMS.Provider: Name of Java Naming Provider (e.g. Websphere)
- JMS.Provider.URL: URL of Java Naming Provider (e.g. ldap://somehost:389)
- JMS.InitialContextFactory: Class name of Initial Context Factory
- JMS.FactoryName: Name used to lookup Queue Connection Factory with Java Naming Provider
- JMS.DestinationQueue.Name: Name used to lookup destination queue with Java Naming Provider
- JMS.DestinationQueue.User: User name used to connect to destination queue
- JMS.DestinationQueue.Password: Password used to connect to destination queue
When delivering a message to queue, the secure messaging channel will create a MapMessage object (javax.jms.MapMessage)
with the following name/value pairs:
- customerID: Set to destination customer id (long value, e.g. 1234567890)
- context: Set to message context string (customer_id.instance_id.event_queue_id or "1234567890.54321.0")
- data: Set to outgoing message in string form
